Beyond the Green Screen: The Rise of Virtual Production Cinematography
In the rapidly evolving world of cinema, every decade has brought a groundbreaking shift in how stories are brought to life. From the golden age of practical effects to CGI-dominated blockbusters, filmmakers have continually pushed the boundaries of visual storytelling.
Today, one of the most exciting transformations in filmmaking is the rise of virtual production cinematography, a revolutionary blend of real-time technology, digital environments, and physical sets that is reshaping the entire industry.
What is Virtual Production?
At its core, virtual production is the integration of real-time technology and visual effects (VFX) during the filmmaking process. Unlike traditional post-production VFX, where CGI is added after filming, virtual production allows filmmakers to create and manipulate digital environments and assets in real-time, often during the shoot itself.
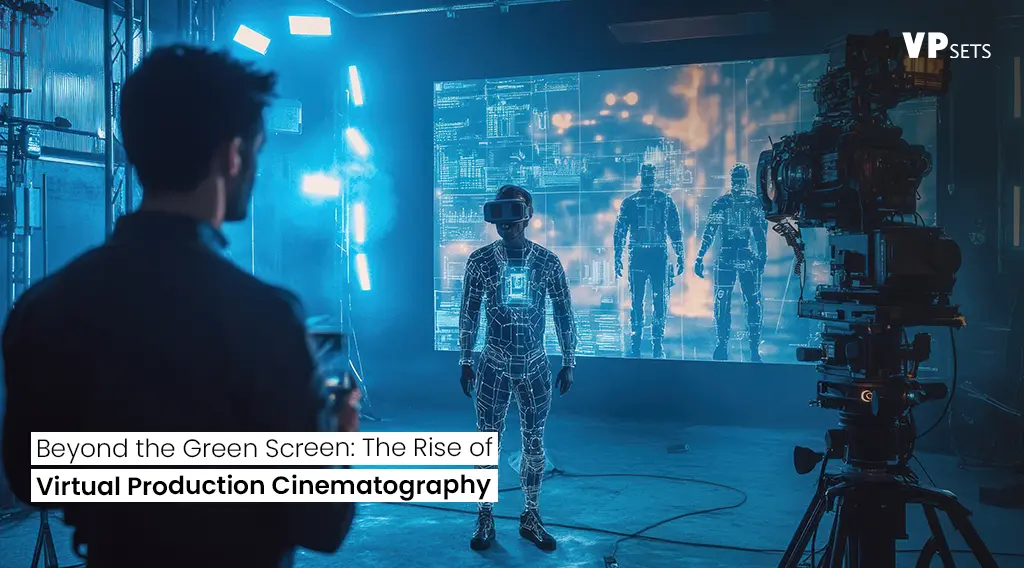
This technology blends physical actors and props with vast, fully realized virtual backgrounds, removing the need for traditional green or blue screens.
One of the key components of virtual production is the use of LED volumes and massive walls of LED screens that project ultra-high-definition digital environments. These LED walls replace green screens and immerse actors in the scene, displaying real-time backgrounds that change with camera movements, lighting, and other dynamic factors.
The Technology Behind the Magic
Virtual production is made possible through cutting-edge game engines like Unreal Engine and Unity, which render high-fidelity 3D environments instantly. These engines were initially developed for video games but have been adapted to create cinematic-quality visuals for film and TV. They allow filmmakers to shoot within virtual worlds, changing everything from landscapes to lighting on the fly.
A prime example of this technology in action is The Mandalorian, one of the first major productions to leverage virtual production extensively. Instead of shooting on location or relying on green screens for complex VFX shots, the filmmakers used large LED walls to create immersive settings, resulting in a more seamless integration of live-action and digital elements.
Key Benefits of Virtual Production
1. Immersive Environments for Actors
One of the biggest criticisms of green screen work is the lack of immersion for actors. Virtual production changes this by placing them directly in the environment they are interacting with. This leads to more authentic performances, as actors can respond naturally to their surroundings rather than imagining what's behind them.
2. Real-Time Adjustments
Directors and cinematographers can make real-time changes to the environment, lighting, or camera angles. Need to adjust the lighting on a sunset? No problem. Want to change the backdrop from a desert to a snowy landscape? Done. This flexibility saves time and budget, reducing the need for expensive and time-consuming reshoots.
3. Reduced Production Costs
While virtual production technology requires a significant upfront investment, it can save substantial money in the long run. The ability to shoot multiple locations without leaving the studio, reducing travel and logistical expenses, is invaluable. It also decreases the reliance on large post-production VFX teams, allowing more of the work to be completed during filming.
4. Environmentally Friendly Filmmaking
In an era where sustainability is becoming a crucial consideration for every industry, virtual production offers an environmentally friendly alternative. By reducing the need for on-location shoots and large-scale set constructions, this technology helps to lower the carbon footprint of film productions.
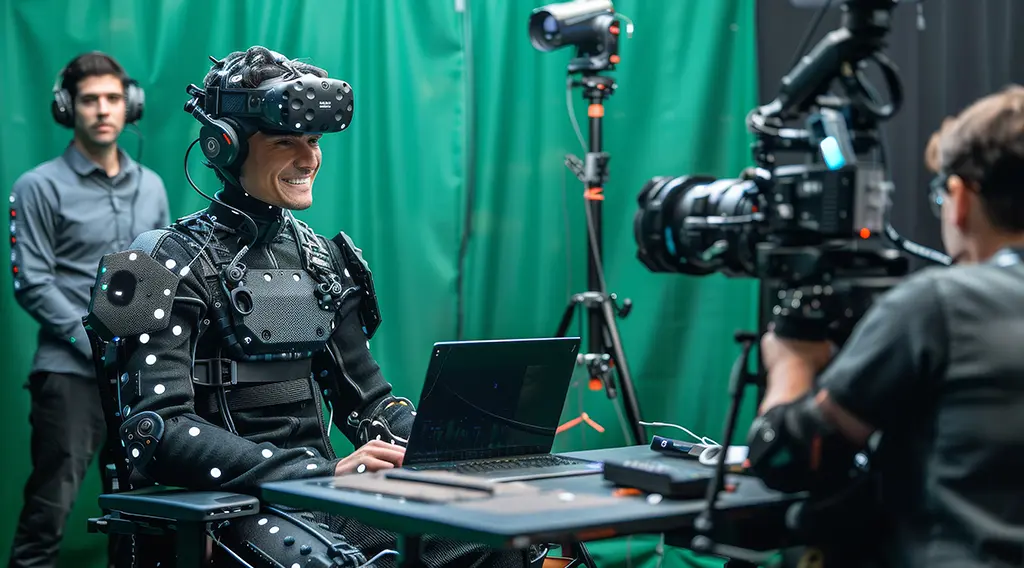

Shaping the Future of Cinema
Virtual production is not just a trend; it represents a paradigm shift in how films and TV shows will be created. As this technology becomes more accessible, filmmakers of all budgets will have the opportunity to experiment with it, democratizing the cinematic landscape.
Moreover, the impact of virtual production extends beyond just large-scale blockbusters.Independent filmmakers, who may not have the resources for large-scale sets or international shoots, can now use virtual production tools to tell expansive stories that previously would have been out of reach.
This opens up new avenues for creative storytelling, allowing indie films to compete visually with studio-driven productions.
Challenges and the Road Ahead
Despite its many advantages virtual production is not without challenges The technology is still in its early stages, and the costs of high-quality LED volumes and the associated hardware can be prohibitive for smaller studios.
Additionally, the learning curve for integrating real-time game engines with traditional film workflows requires a new skill set for filmmakers.
However, as more productions adopt virtual production techniques, the technology is expected to become more affordable and accessible. The success of projects like The Mandalorian has proven that virtual production is not just a novelty but a viable way to create compelling visual stories.
Major studios are investing heavily in this space, and it’s only a matter of time before it becomes a standard part of the filmmaking toolkit.
Conclusion
Virtual production cinematography is ushering in a new era of filmmaking, where the limitations of physical space and time are dissolved. As the technology continues to evolve, it promises to unlock new creative possibilities, streamline production workflows, and make the impossible possible on screen.
Beyond the green screen lies a future where filmmakers can create anything they can imagine, bringing their most ambitious visions to life with unprecedented realism. This is the beginning of a cinematic revolution, and it’s only just getting started.
